- Site Navigation -
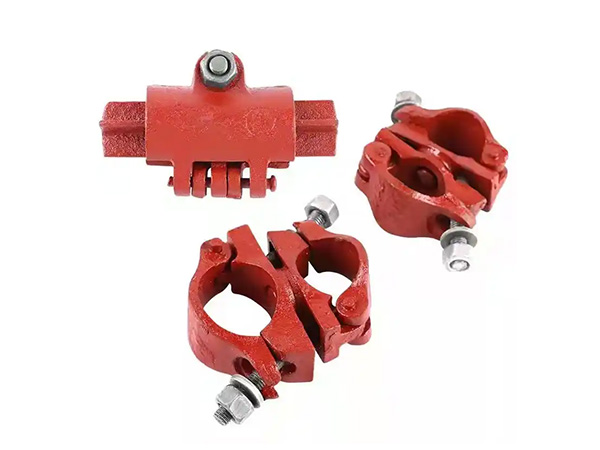

Malleable Cast Iron Fastener
A Malleable Cast Iron Fastener refers to a type of hardware component(such as bolts,nuts,clamps,or couplers)manufactured from malleable cast iron,a material known for its unique com......
A Malleable Cast Iron Fastener refers to a type of hardware component(such as bolts,nuts,clamps,or couplers)manufactured from malleable cast iron,a material known for its unique combination of strength,ductility,and cost-effectiveness.These fasteners are widely used in applications requiring robust mechanical properties and resistance to deformation under stress.
Key Characteristics of Malleable Cast Iron
Material Properties:
Ductility:Unlike brittle white cast iron,malleable cast iron undergoes heat treatment(annealing)to convert carbon into temper carbon nodules,granting it greater toughness and ability to deform without fracturing.
Strength:Tensile strength typically ranges from 350 to 450 MPa,with good yield strength and impact resistance.
Machinability:Easier to machine and shape compared to other cast irons.
Corrosion Resistance:
Often coated with galvanization,epoxy,or paint to enhance corrosion resistance,as bare cast iron is susceptible to rust.
Common Types of Fasteners Made from Malleable Cast Iron
Scaffolding Couplers:
Right-angle couplers,swivel couplers,and sleeve couplers used in construction scaffolding.
Pipe Clamps and Hangers:
Supports for plumbing,HVAC,and industrial piping systems.
Beam Clamps:
Used to attach utilities to structural steel beams.
Electrical Conduit Fittings:
Connectors and locknuts for electrical conduits.
Custom Brackets and Hardware:
Components requiring complex shapes and moderate load-bearing capacity.
Advantages
Cost-Effective:Lower production costs compared to steel forgings or stainless steel.
Good Strength-to-Weight Ratio:Suitable for medium-to-heavy-duty applications.
Vibration Resistance:Absorbs shocks and vibrations better than brittle materials.
Design Flexibility:Can be cast into intricate shapes without extensive machining.
Limitations
Not for High-Stress Applications:Less strong than forged steel;not ideal for extreme loads or dynamic tension.
Corrosion Vulnerability:Requires protective coatings for outdoor or humid environments.
Temperature Sensitivity:Loses strength at elevated temperatures(>400°C).
Manufacturing Process
Casting:Molten iron is poured into molds to form rough shapes.
Annealing:Cast parts are heat-treated at~900°C to convert brittle cementite into ductile temper carbon.
Machining:Final threading,drilling,or surface finishing is applied.
Coating:Galvanization or other anti-corrosion treatments are added.
Applications
Construction:Scaffolding systems,pipe supports,and structural brackets.
Industrial Machinery:Mounting components,gear housings,and machinery frames.
Infrastructure:Railings,drainage grates,and utility supports.
Agriculture:Equipment parts requiring durability and moderate strength.
Standards and Compliance
ASTM A47:Standard specification for malleable iron castings.
EN 1562:European standard for malleable cast iron materials.
ISO 5922:International standard for malleable cast iron.