- Site Navigation -

Scaffold Fittings
Scaffold fittings are core connecting and supporting components of scaffold systems. They are mainly used to assemble the main structural members of scaffolds (such as vertical pole......
Scaffold fittings are core connecting and supporting components of scaffold systems. They are mainly used to assemble the main structural members of scaffolds (such as vertical poles, horizontal poles, and diagonal poles) into stable working platforms. These fittings ensure that scaffolds have sufficient load-bearing capacity and stability in scenarios such as building construction, maintenance, and decoration, serving as crucial components to guarantee the safety of construction workers during operations. Their quality and compatibility directly affect the overall structural safety of scaffolds, and they are widely used in various construction scenarios including residential buildings, commercial buildings, and bridge projects.
I. Core Types and Functions
Based on different connection methods and functions, scaffold fittings can be divided into four major categories. Each type of fitting has a clear role, working together to form a stable scaffold structure:
Connection Fittings
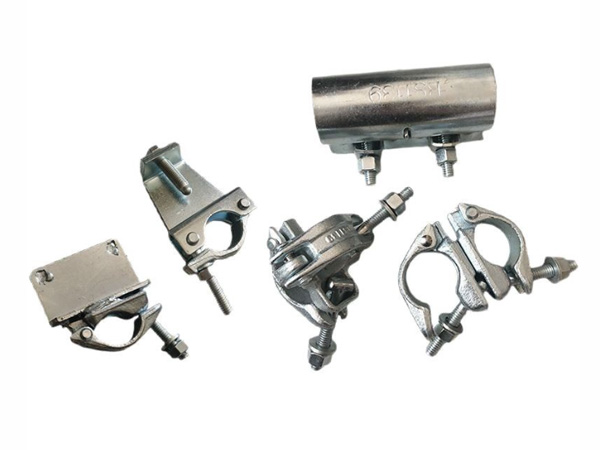
Couplers: The most commonly used connecting components, divided into right-angle couplers (for vertical connection between vertical poles and horizontal poles), swivel couplers (for connection between horizontal poles and diagonal poles at any angle), and sleeve couplers (for extension connection of vertical poles or horizontal poles in the same straight line). The mainstream materials are malleable cast iron (e.g., QT450-10) or stamped steel plates. The surface is treated with hot-dip galvanization for rust prevention, and they must have sufficient anti-slip and anti-damage performance (e.g., the anti-slip load-bearing capacity of right-angle couplers is ≥7.5kN).
Clamps: Designed for special scenarios, such as wall clamps (used to fix scaffolds to building walls to enhance overall stability) and pipe clamps (used to fix temporary pipelines or protective nets). They are mostly made of stainless steel or high-strength carbon steel, compatible with scaffold pipes of different diameters.
Support Fittings
Base Plates: Installed at the bottom of scaffold vertical poles, divided into fixed base plates (directly placed on the ground with anti-slip patterns at the bottom) and adjustable base plates (equipped with screws, adjustable in height to adapt to uneven ground, with a common adjustment range of 100-300mm). They are mostly made of thick steel plates (thickness ≥6mm), and the bottom area must be large enough (e.g., 150mm×150mm) to prevent vertical poles from sinking into the ground.
Ledgers & Transoms: Although they are extensions of main structural members, dedicated connecting fittings (such as ledger joints) can enhance the connection strength between ledgers/transoms and vertical poles. Some fittings are equipped with positioning pins to prevent horizontal displacement of horizontal poles and ensure the flatness of the working platform.
Protective Fittings
Guard Rail Brackets: Used to install protective railings on the outer side of scaffolds. Most of them adopt a snap-on design, which can be quickly fixed on horizontal poles and adapted to protective needs of different heights (e.g., 1.2m main guardrail and 0.6m secondary guardrail from the ground). The material must be consistent with that of couplers to ensure impact resistance.
Toe Board Brackets: Fittings used to fix toe boards (to prevent tools and materials from falling). They are usually slot-type and can be directly clamped on scaffold vertical poles or horizontal poles, with a height ≥180mm, avoiding safety accidents caused by falling construction debris.
Auxiliary Fittings
Scaffold Wheels: Used for mobile scaffolds. The wheel body is mostly made of rubber (wear-resistant and quiet) and equipped with a braking device (to prevent the scaffold from sliding after locking). They are compatible with light-duty scaffolds (load-bearing ≤500kg), facilitating flexible movement in scenarios such as interior decoration.
Lifting Lugs: Used for integral hoisting of large-scale scaffolds. Made of high-strength alloy steel, they must undergo flaw detection to ensure no fracture occurs during hoisting. They are suitable for high-altitude construction scenarios such as bridges and large workshops.
II. Core Performance Requirements and Standards
Scaffold fittings must comply with strict industry standards to ensure safety and reliability:
Material Standards: Malleable cast iron couplers must conform to GB 15831-2006 Steel Pipe Scaffold Couplers, with a tensile strength ≥335MPa; stamped steel couplers must meet anti-deformation and anti-fatigue requirements, and the thickness of the surface galvanized layer must be ≥85μm for rust prevention (service life ≥5 years).
Load-Bearing Performance: The anti-slip load-bearing capacity of right-angle couplers is ≥7.5kN, the tensile load-bearing capacity of sleeve couplers is ≥4.0kN, and the compressive load-bearing capacity of base plates must match the load of scaffold vertical poles (e.g., when the spacing of vertical poles is 1.5m, the compressive capacity of base plates is ≥15kN).
Safety Certification: Regular products must pass third-party testing (such as load testing and fatigue testing) and be marked with the manufacturer's logo, model, production date, and other information. The use of uncertified inferior fittings (such as brittle cast iron couplers and thin steel base plates) is prohibited.
III. Key Points for Selection and Safe Use
Selection Compatibility: Select corresponding fittings according to the type of scaffold (e.g., coupler-type steel pipe scaffolds, frame scaffolds). For example, couplers must be compatible with the diameter of steel pipes (common φ48.3mm steel pipes, with the inner diameter of fittings requiring precise matching and a gap ≤0.5mm); the adjustment range of adjustable base plates must cover the height difference of the construction ground to avoid reduced stability due to excessive adjustment.
Installation Specifications: Couplers must be tightened (the bolt tightening torque is 40-65N·m; insufficient tightness may cause slipping, while excessive tightness may cause fracture); base plates must be placed on flat and hard ground (or padded with steel plates and square timbers) to avoid uneven settlement; protective fittings must be fully installed (e.g., full installation of guardrails and toe boards on the outer side of scaffolds) without omissions.
Daily Inspection: Before use, check whether fittings have cracks, deformation (such as cracks at the opening of couplers, bending of base plate steel plates), and rust (replace if the galvanized layer falls off by ≥10%); during use, regularly recheck the tightness of couplers and the settlement of base plates, and immediately stop using and replace fittings if problems are found.
Prohibited Scenarios: It is prohibited to use fittings in scenarios beyond their load-bearing range (e.g., using light-duty couplers to connect heavy-duty scaffolds); mixing fittings of different materials and specifications is prohibited (e.g., mixing cast iron couplers with steel plate couplers, which may cause fracture due to uneven stress); welding or cutting fittings is prohibited (as this damages the original structural strength).
IV. Summary
Although scaffold fittings are "small components" of scaffold systems, they are "critical for safety" in construction. With diverse types and specialized functions, they require strict compliance with standards for selection, standardized installation, and regular maintenance to ensure the overall structural stability of scaffolds and provide a safe and reliable working platform for construction workers. In construction projects, attaching importance to the quality and safe use of scaffold fittings is a core measure to prevent accidents such as scaffold collapse and falls.