- Site Navigation -

Scaffolding Coupler
A scaffolding coupler(also known as a scaffold clamp)is a specialized connecting component designed to fasten the main structural elements of a scaffold—such as vertical poles,hor......
A scaffolding coupler(also known as a scaffold clamp)is a specialized connecting component designed to fasten the main structural elements of a scaffold—such as vertical poles,horizontal ledgers,and diagonal braces—into a stable,load-bearing framework.As the"joint"of the scaffold system,its quality and proper installation directly determine the overall structural integrity and safety of the scaffold,making it indispensable in construction,maintenance,and renovation projects.Scaffolding couplers must withstand static loads(e.g.,the weight of workers and materials)and dynamic forces(e.g.,wind pressure and accidental impacts),requiring strict compliance with industry standards for performance and durability.
I.Main Types and Functional Applications
Scaffolding couplers are classified based on their connection angle and purpose,with three primary types dominating construction sites,each tailored to specific assembly needs:
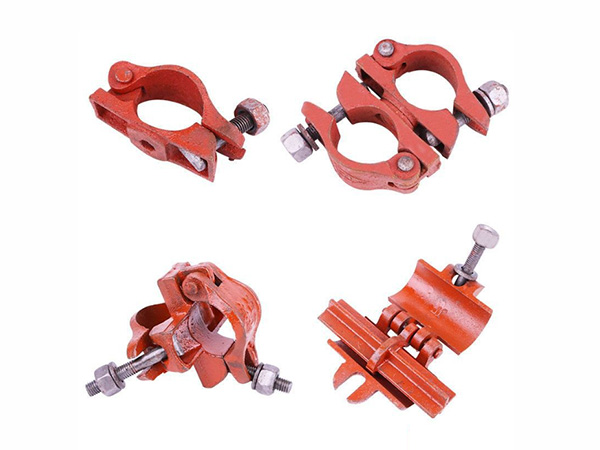
Right-Angle Coupler(Vertical Coupler)
Function:Specifically designed for the perpendicular connection between vertical poles(standards)and horizontal ledgers.It ensures that horizontal members remain firmly attached to vertical supports,forming the basic"grid"of the scaffold platform.
Design Features:Features a U-shaped body with two clamping bolts—one for the vertical pole and one for the horizontal ledger.The inner surface of the clamp is often textured or lined with anti-slip rubber to enhance friction and prevent slippage under load.
Typical Application:Used in the main framework of all types of coupler-type steel pipe scaffolds,such as assembling floor platforms and vertical support columns.
Swivel Coupler(Universal Coupler)
Function:Enables connection between two scaffold pipes at any angle(ranging from 0°to 180°),making it ideal for attaching diagonal braces(struts)to vertical poles or horizontal ledgers.Diagonal braces reinforced with swivel couplers improve the scaffold’s lateral stability,resisting sway caused by wind or uneven loads.
Design Features:The coupler body consists of two rotatable clamping heads connected by a hinge,allowing flexible adjustment of the pipe angle.After positioning,the bolts are tightened to lock the angle in place,ensuring no rotation during use.
Typical Application:Installing diagonal bracing in high-rise scaffolds,reinforcing corner joints,or connecting pipes in irregularly shaped scaffold structures(e.g.,around building protrusions).
Sleeve Coupler(Joining Coupler)
Function:Used to extend the length of scaffold pipes(both vertical poles and horizontal ledgers)by connecting two pipes end-to-end in a straight line.It ensures the extended pipe maintains uniform load-bearing capacity without weakening at the joint.
Design Features:Available in two styles—internal sleeve couplers(a cylindrical sleeve inserted inside the ends of two pipes)and external sleeve couplers(a sleeve that wraps around the outer circumference of the pipe ends).Both types use bolts to secure the connection,with alignment marks to ensure the pipes are perfectly straight.
Typical Application:Extending vertical poles in tall scaffolds(e.g.,for high-rise building construction)or lengthening horizontal ledgers to cover wider spans between vertical supports.
II.Material Selection and Performance Standards
To meet the rigorous demands of construction sites,scaffolding couplers must be manufactured from high-performance materials and adhere to strict quality standards:
Common Materials
Malleable Cast Iron(e.g.,QT450-10):The most widely used material,valued for its high tensile strength(≥335MPa),good ductility,and impact resistance.It can withstand repeated tightening and loosening without brittle fracture,making it suitable for long-term,repeated use.
Stamped Steel Plate:Made from high-strength carbon steel(e.g.,Q235)through stamping and welding.It offers lighter weight than cast iron and excellent corrosion resistance when coated with hot-dip galvanization,ideal for humid or coastal construction environments.
Stainless Steel(e.g.,304,316):Used in specialized scenarios(e.g.,food processing plants,chemical facilities)where corrosion resistance is critical.It resists rust from chemicals or moisture but is more costly,limiting its use to high-demand applications.
Key Performance Requirements
Anti-Slip Capacity:For right-angle couplers,the anti-slip load-bearing capacity must be≥7.5kN to prevent horizontal ledgers from sliding down vertical poles under load.
Tensile Strength:Sleeve couplers must withstand a tensile load of≥4.0kN without breaking,ensuring the connected pipes do not separate under tension.
Corrosion Resistance:Surface treatment(e.g.,hot-dip galvanization with a coating thickness≥85μm)is required to resist rust and extend service life to≥5 years in typical construction environments.
Standard Compliance:Must meet international standards such as GB 15831-2006(China),EN 74-1(Europe),or ANSI/ASSE A10.8(USA),with third-party testing certificates to verify performance.
III.Installation Safety and Maintenance Guidelines
Improper installation or maintenance of scaffolding couplers is a major cause of scaffold accidents.The following practices are essential for safe use:
Installation Precautions
Bolt Tightening Torque:Use a torque wrench to tighten bolts to the specified range(40-65N·m).Under-tightening can cause slippage,while over-tightening may damage the coupler or strip the bolt threads.
Pipe Compatibility:Ensure the coupler matches the pipe diameter(common size:φ48.3mm).A gap of more than 0.5mm between the coupler and pipe can reduce stability and increase the risk of failure.
Load Distribution:Avoid concentrating excessive load on a single coupler.Distribute loads evenly across multiple couplers and ensure diagonal braces are installed to share lateral forces.
Daily Inspection and Maintenance
Pre-Use Inspection:Check for cracks in the coupler body,bent bolts,or worn anti-slip surfaces.Replace any coupler with visible damage(e.g.,cracks at the bolt holes)immediately.
Corrosion Check:Inspect the galvanized coating for peeling or rust.If the rusted area exceeds 10%of the surface,the coupler must be replaced to prevent structural failure.
Post-Use Maintenance:Clean couplers of dirt,concrete,or debris after use.Apply anti-rust oil to bolts to prevent seizing,and store them in a dry,ventilated area to avoid moisture damage.
IV.Selection Tips for Different Scenarios
Choosing the right scaffolding coupler depends on the scaffold type,environment,and load requirements:
General Construction Sites:Opt for malleable cast iron couplers(QT450-10)for their balance of strength and cost-effectiveness.
Humid/Coastal Areas:Select hot-dip galvanized stamped steel couplers to resist corrosion from saltwater or moisture.
Chemical/Food Industry:Use stainless steel couplers to withstand chemical exposure and meet hygiene standards.
High-Rise Scaffolds:Prioritize couplers with enhanced anti-slip performance(e.g.,rubber-lined right-angle couplers)and sleeve couplers with alignment guarantees to ensure vertical stability.
V.Summary
Scaffolding couplers are the"backbone"of scaffold stability,enabling the assembly of safe,reliable working platforms.By understanding their types,materials,and performance standards,and following strict installation and maintenance practices,construction teams can minimize accident risks and ensure scaffold systems meet the demands of even the most challenging projects.Investing in high-quality,compliant couplers is not just a regulatory requirement—it is a critical step in protecting the safety of construction workers.