- Site Navigation -
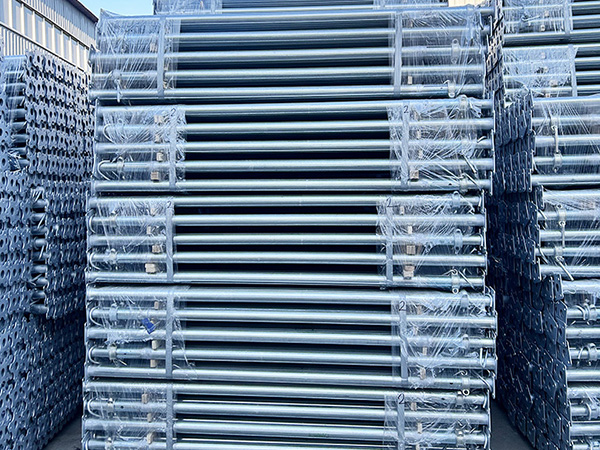

Inclined Steel Support
Inclined Steel Support,also called diagonal steel brace or angled steel prop,is a specialized load-bearing component designed to resist lateral,horizontal,or inclined forces in cons......
Inclined Steel Support,also called diagonal steel brace or angled steel prop,is a specialized load-bearing component designed to resist lateral,horizontal,or inclined forces in construction,infrastructure,and industrial projects.Unlike vertical supports that primarily bear vertical loads,it is installed at an angle(typically 30°-60°to the horizontal/vertical)to provide tensile and compressive stability,preventing structural deformation,sway,or collapse caused by wind loads,seismic activity,or uneven construction loads.Made of high-strength steel,it is widely used in scaffold systems,formwork bracing,steel structure assembly,and temporary infrastructure support—serving as a"stabilizing backbone"for both temporary and semi-permanent structures.Its key advantages include strong lateral load resistance,flexible installation angles,and compatibility with various structural components,making it indispensable for ensuring overall structural safety.
Core Design&Structural Features
Inclined Steel Support is engineered for"force transmission efficiency"and"installation flexibility,"with structural details optimized to handle multi-directional loads:
High-Strength Material:Primarily constructed from Q235/Q355 carbon steel or S355JR alloy steel(for high-demand scenarios),available in forms of seamless steel tubes(common diameters:Φ48mm,Φ60mm,Φ89mm,wall thickness 3mm-5mm),angle steels(L50×5-L100×10),or channel steels(C10-C20).The material selection ensures excellent tensile(≥375MPa)and compressive strength,with galvanized or painted surfaces for corrosion resistance(critical for outdoor or humid environments).
Adjustable Connection Joints:Equipped with universal hinges,swivel couplers,or threaded ends to adapt to different installation angles and structural connections.For example,swivel couplers(compatible with scaffold tubes)allow 360°rotation,enabling precise alignment with vertical/horizontal components;threaded ends(M16-M24)enable length fine-tuning(adjustment range 50mm-300mm)to compensate for installation errors.
Load-Bearing Plates&Anchors:At both ends,it features rectangular or circular bearing plates(100×100mm-150×150mm,thickness≥5mm)to distribute inclined forces evenly onto connected structures(e.g.,scaffold立杆,concrete walls).For ground-mounted applications,bottom ends may include expansion bolts or ground anchors to secure the support to concrete or solid substrates,preventing slippage.
Reinforced Joints:Welded triangular ribs or stiffening plates at connection points(e.g.,plate-tube junctions)to enhance shear resistance,avoiding joint failure under alternating tensile/compressive loads(common in dynamic scenarios like wind-induced sway).
Main Classification
By Application Scenario:
Scaffold Diagonal Braces:Used in scaffold systems(cuplock,or frame-type)to resist lateral wind loads and prevent scaffold tilting.Typically installed in a"X"or"V"pattern between vertical立杆s,with standard lengths ranging from 1.5m-3m.
Formwork Inclined Supports:Brace for beam,column,or wall formwork to counteract concrete lateral pressure(e.g.,during wall pouring,concrete exerts 20-50kN/m²lateral force).Adjustable models with swivel joints adapt to formwork slopes(e.g.,sloped walls in stadiums).
Steel Structure Temporary Bracings:Support for prefabricated steel beams,trusses,or columns during installation,preventing structural deformation before permanent welding or bolting.Heavy-duty types(using channel steels)handle loads up to 50kN.
By Adjustability:
Fixed-Length Inclined Supports:Pre-cut to standard lengths(e.g.,2m,2.5m)for scenarios with consistent angles and distances,suitable for large-scale standardized construction.
Adjustable Inclined Supports:With telescopic tubes or threaded rods for length/angle adjustment,ideal for complex or irregular structures(e.g.,curved walls,sloped roofs)where fixed-length supports cannot fit.
Typical Applications
Building Construction:In high-rise residential or commercial projects,installed as diagonal braces in scaffold systems to resist wind loads(up to 0.4kN/m²)and prevent scaffold collapse;for shear wall formwork,used to counteract concrete lateral pressure and ensure formwork alignment.
Infrastructure Projects:In bridge construction,supports precast beam segments during hoisting and installation,preventing lateral displacement;in tunnel projects,braces tunnel linings or temporary shotcrete walls to resist soil pressure(common in soft soil tunnels).
Industrial&Renovation Works:In factory workshops,braces heavy steel equipment(e.g.,cranes,conveyors)during maintenance;in heritage building renovation,non-destructive inclined supports(with padded ends)stabilize fragile walls or arches without damaging historic structures.
Usage&Safety Guidelines
Angle&Load Calculation:Determine installation angle(optimally 45°for maximum force transmission)and select support specifications based on calculated lateral loads(using software like SAP2000 or ETABS).Never use undersized supports—e.g.,aΦ48mm tube brace(rated 15kN)cannot replace aΦ60mm one(rated 25kN)for high-load scenarios.
Secure Connection:Ensure both ends are firmly fixed—swivel couplers must be tightened to torque requirements(35-50N·m for scaffold couplers);ground anchors must be embedded to sufficient depth(≥100mm in concrete)to resist pull-out forces.
Avoid Overloading:Do not use inclined supports to bear vertical loads(beyond 10%of their rated lateral load);overloading may cause buckling(for compressive loads)or stretching(for tensile loads).
Inspection&Maintenance:Before use,check for material defects(cracks,bending,rust),loose joints,or worn threads—replace supports with bent tubes(bending degree>L/500,L=support length)or damaged couplers.After use,clean and store in a dry area,re-galvanizing or repainting corroded surfaces to extend service life.
Symmetric Installation:In scaffold or formwork systems,install inclined supports symmetrically(e.g.,equal numbers on both sides of a wall)to ensure balanced force distribution,avoiding one-sided stress concentration.