- Site Navigation -
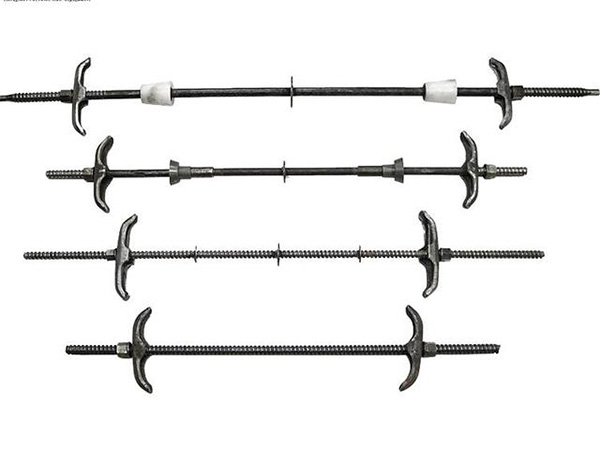

All-Thread Rod
An All-Thread Rod(also commonly known as Threaded Rod,All-Thread,Studding,or Continuous Threaded Bar)is a versatile cylindrical fastener characterized by having a continuous,uniform......
An All-Thread Rod(also commonly known as Threaded Rod,All-Thread,Studding,or Continuous Threaded Bar)is a versatile cylindrical fastener characterized by having a continuous,uniform thread running along its entire length.It serves as a fundamental building block in construction,manufacturing,and electrical industries,functioning as a customizable-length bolt,a structural tie,or a component for creating modular frameworks.
Its primary value lies in its adaptability;it can be cut to any desired length and combined with nuts and washers to create a virtually infinite variety of fastening solutions.
Key Features&Design:
Continuous Threading:The defining feature is the uninterrupted external thread from one end of the rod to the other.This allows nuts to be positioned and secured at any point along the rod.
Materials and Finishes:Available in a wide range of materials to suit different environments and strength requirements:
Carbon Steel:The most common type,often with a zinc-plated finish for corrosion resistance.
Stainless Steel:(Grades 304 and 316)For superior corrosion resistance in outdoor,marine,or chemical environments.
Hot-Dip Galvanized:For heavy-duty outdoor and industrial applications.
Brass and Aluminum:Used for decorative purposes or in non-magnetic/electrical applications.
Grades and Strength:Like bolts,they are manufactured to various strength grades(e.g.,ASTM A36,Grade 2,Grade 5,Grade 8,and A193-B7 for high-temperature applications),indicating their tensile and yield strength.
Diameters and Lengths:Standardly available in imperial(inch)and metric diameters.They are sold in long,straight lengths(typically 3,6,10,or 12 feet)that can be cut to size.
How It Is Used:
The functionality is derived from its combination with other hardware:
As a Long Bolt:Cut to length,it can be used with two nuts to fasten objects together,effectively acting as a bolt of any size.
As a Hanger Rod:Commonly used to suspend electrical conduit,piping,HVAC ductwork,and ceiling grids from overhead structures.A nut is secured at the desired height on the rod to support a strap or bracket.
As a Structural Tie:Used in through-bolt applications(as previously described)to connect structural elements across a wall or cavity,secured with nuts and bearing plates on both ends.
As a Threaded Stud:One end can be anchored into a wall using an epoxy anchor or a female anchor(like a drop-in anchor),while the exposed threads are used to mount equipment or panels.
To Make Standoffs and Spacers:Used to create space between two objects by placing a sleeve over the rod and securing it with nuts on either side.
Common Applications:
Construction:Creating through-wall ties,anchoring sill plates to foundations,and securing structural frames.
Electrical:The most common application is as threaded rod for hanging cable trays,conduit,and junction boxes.
Mechanical/Piping:Supporting and bracing pipe runs and mechanical equipment.
Manufacturing:Assembling machinery,fabricating jigs,and creating adjustable frameworks.
Retail and Display:Constructing modular shelving systems and display units.
Advantages:
Ultimate Flexibility:Can be customized on-site to any length,eliminating the need to stock bolts of every conceivable size.
Cost-Effective:A single length of rod can be cut into multiple fasteners for various jobs,reducing material waste and inventory costs.
High Strength:Available in high-strength grades suitable for demanding structural applications.
Ease of Assembly and Adjustment:Nuts can be easily moved and re-positioned along the thread,allowing for fine-tuning and alignment.
Installation and Handling:
Cutting:Can be easily cut to length with a reciprocating saw,band saw,or angle grinder with a cut-off wheel.
Thread Protection:The ends are often sharp after cutting;thread-protector nuts or caps can be used to protect the threads and prevent injury.
Nut Driving:Nuts can be run along the length of the rod using a power drill with a nut-setter attachment,significantly speeding up installation.