- Site Navigation -
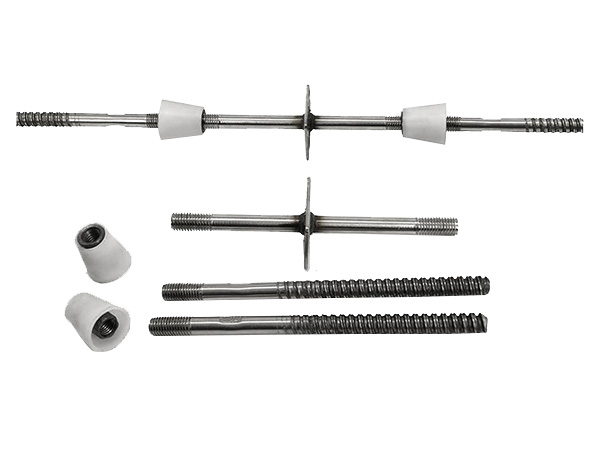

Double-Ended Through-Bolt
A double-ended through-bolt is a specialized fastener engineered for applications requiring secure,load-bearing connections between two or more components.......
A double-ended through-bolt is a specialized fastener engineered for applications requiring secure,load-bearing connections between two or more components.Characterized by threaded segments on both ends with an unthreaded shank in the middle,this bolt design enables precise clamping force distribution and versatility across industrial,construction,and manufacturing contexts.Typically constructed from high-grade carbon steel,stainless steel(304/316),or alloy steel(e.g.,Grade 8.8,10.9),its material selection is dictated by environmental conditions,load requirements,and corrosion resistance needs.
Design and Dimensions
The defining feature of a double-ended through-bolt is its symmetrical threading,with thread pitches conforming to international standards such as ISO metric(M-series)or UNC/UNF(imperial).Thread lengths range from 25%to 50%of the total bolt length,while the unthreaded shank diameter—often larger than the root diameter of the threads—enhances shear strength.Diameters commonly span from M6(1/4 inch)to M64(2.5 inches),with lengths up to 3 meters for heavy-duty applications.Headless configurations are standard,though some variants include hexagonal or square heads on one end for rotational stability during installation.
Mechanical Properties
Engineered for structural integrity,these bolts exhibit tensile strengths from 400 MPa(Grade 4.6)to 1,200 MPa(Grade 12.9),with yield strengths ranging from 240 MPa to 1,080 MPa.Fatigue resistance is optimized through rolled threading(improving grain flow)and heat treatment processes like quenching and tempering.The shank’s smooth surface minimizes stress concentration,making it suitable for dynamic load applications such as machinery mounts or bridge bracing.
Installation and Assembly
Installation involves inserting the bolt through pre-drilled aligned holes in the connected components,followed by tightening nuts on both ends using torque wrenches to achieve specified clamping forces.Washers(flat,lock,or spring)are often used to distribute pressure,prevent surface damage,and resist loosening under vibration.For critical joints,thread-locking compounds(e.g.,Loctite)or mechanical locking devices may be applied.The double-ended design allows for incremental adjustment during assembly,facilitating precise alignment in structural frameworks.
Applications
Construction:Securing steel beams,concrete formwork,and precast panels.Stainless steel variants are preferred for coastal or high-moisture environments to prevent corrosion.
Heavy Machinery:Mounting engines,gearboxes,and hydraulic systems,where high shear and tensile loads are encountered.
Infrastructure:Bridge expansion joints,tunnel supports,and railway track fastenings,often utilizing hot-dip galvanized bolts for outdoor durability.
Oil&Gas:Pipeline flanges and offshore platform structures,where API-certified alloys(e.g.,A193 B7)ensure resistance to extreme temperatures and pressure.
Renewable Energy:Wind turbine tower assemblies and solar panel racking systems,requiring vibration-resistant connections.
Corrosion Protection
To extend service life in harsh environments,double-ended through-bolts employ various surface treatments:
Zinc Plating:Provides basic protection for indoor applications,with a typical thickness of 5–15μm.
Hot-Dip Galvanizing:Creates a 50–100μm zinc coating for outdoor use,offering superior resistance to saltwater and industrial chemicals.
Electroless Nickel Plating:Delivers uniform coverage for precision components,combining corrosion resistance with low friction.
Epoxy Coating:Ideal for aggressive environments like wastewater treatment plants,providing a thick,chemical-resistant barrier.
Standards and Compliance
Manufacturing adheres to global standards including ISO 898-1(mechanical properties),ASTM A307(carbon steel),ASTM A193(alloy steel bolts for high-temperature service),and DIN 975(threaded rods).Quality control involves tensile testing,hardness checks(Rockwell/Brinell),and dimensional verification to ensure conformance with specifications.
Advantages Over Alternatives
Compared to single-ended bolts or threaded rods,double-ended through-bolts offer:
Balanced Clamping:Symmetrical threading ensures uniform force distribution across joint surfaces.
Adjustability:Independent nut tightening allows for micro-adjustments during alignment.
High Load Capacity:The unthreaded shank provides greater shear strength than fully threaded rods.
Versatility:Compatible with a wide range of nuts,washers,and accessories for customized solutions.
Limitations and Considerations
Installation Access:Requires clearance on both ends for nut tightening,which may restrict use in confined spaces.
Cost:Higher material and manufacturing costs compared to standard bolts,though offset by performance benefits in critical applications.
Corrosion Monitoring:In marine or industrial settings,regular inspection for coating degradation or thread pitting is necessary to prevent failure.
In summary,the double-ended through-bolt stands as a reliable,high-performance fastening solution,combining mechanical robustness with adaptability across diverse industries.Its design evolution continues to focus on material innovation(e.g.,titanium alloys for aerospace)and enhanced corrosion protection,ensuring its relevance in modern engineering challenges.