- Site Navigation -
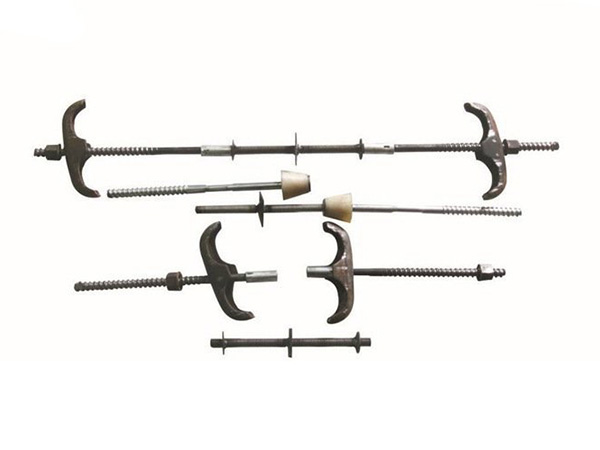

Dual-End Tie Rod
A Dual-End Tie Rod is a heavy-duty,tension-load fastener characterized by having a central unthreaded shank and threaded sections of precisely controlled length on both ends.......
Dual-End Tie Rod:English Introduction
A Dual-End Tie Rod is a heavy-duty,tension-load fastener characterized by having a central unthreaded shank and threaded sections of precisely controlled length on both ends.It is engineered for applications where a component needs to be precisely positioned and securely clamped between two nuts on each end,or where the tie rod must interface with threaded components on both sides.
Its design prioritizes precise assembly,high tensile strength,and the ability to withstand dynamic loads and vibrations without loosening.
Key Features&Design:
Dual-End Threading:The rod features a smooth,often precision-ground,central shank.The ends are threaded,with the threaded length being a specific,controlled dimension rather than running the full length of the rod.
High-Strength Materials:Typically manufactured from high-grade alloy steels(e.g.,Grade 8,ASTM A193 B7),often heat-treated,and finished with a corrosion-resistant coating like zinc plating or hot-dip galvanizing.Stainless steel is common for marine or food-processing applications.
Precision Manufacturing:The transition between the shank and the thread(the"thread relief")is precisely machined to avoid stress concentration and allow nuts to be wrenched fully against a shoulder.
Shouldered Design:The unthreaded shank acts as a shoulder,allowing components to be positioned against it.When a nut is tightened against this shoulder,it provides a known,fixed clamping location and greatly increases the fatigue resistance of the assembly.
How It Works:The Principle of Shouldered Clamping
The dual-end tie rod functions by creating a rigid,precisely located assembly:
The smooth central shank passes through aligned holes in the components being joined.
The threaded ends protrude from the assembly.
Nuts are threaded onto each end and tightened against the components or against washers.
As the nuts are torqued,the unthreaded shank carries the shear load,while the threaded ends are placed in tension to provide the clamping force.
The shoulder ensures the components are correctly located and prevents over-tightening the nuts onto the weaker threaded section.
Common Applications:
Industrial Machinery:A quintessential application is in the assembly of die sets in stamping presses,where they act as guide rods or pillars.They are also used to hold together the platens of hydraulic presses.
Engine and Powertrain Assembly:Used as head studs or main bearing cap studs in engines,where precise clamping force is critical for sealing and alignment.
Structural Framing:Connecting structural elements in heavy fabrications where a shouldered connection is required for accuracy and strength.
Fluid Power:Used as tie rods in the construction of hydraulic and pneumatic cylinders,holding the end caps onto the barrel tube under extreme internal pressure.
Advantages:
Superior Fatigue Resistance:The smooth shank eliminates the stress concentration found at the root of threads,making it far more resistant to dynamic and vibrational loads than a fully threaded rod.
Precise Positioning:The shoulder allows for exact positioning of components,ensuring consistent alignment in automated machinery.
Controlled Clamping:Nuts are tightened against the strong shank,not the threads,allowing for higher and more accurate preload(clamping force).
Increased Shear Strength:The larger diameter of the smooth shank provides higher resistance to shear forces compared to the threaded diameter.