- Site Navigation -
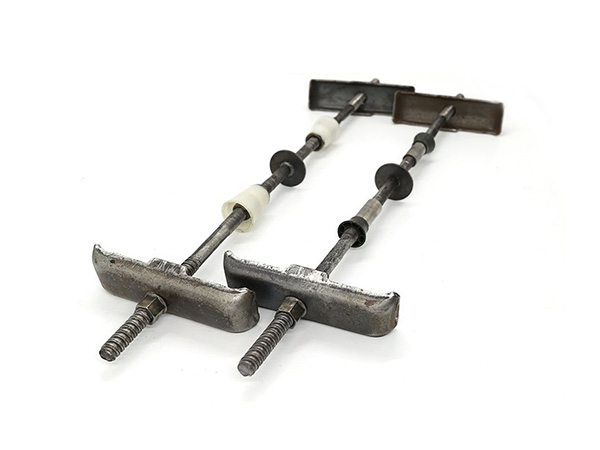

Sleeved Tie Rod
A Sleeved Tie Rod is a specialized tensioning system consisting of a high-strength threaded rod enclosed within a protective sleeve.......
Sleeved Tie Rod:Technical Overview
1.Definition&Purpose
A Sleeved Tie Rod is a specialized tensioning system consisting of a high-strength threaded rod enclosed within a protective sleeve.Designed for applications requiring corrosion resistance,electrical isolation,or adjustable pre-tensioning,it is commonly used in civil engineering,industrial machinery,and seismic reinforcement.The sleeve acts as a barrier against environmental damage while allowing the rod to function as a structural tie.
2.Key Components
Central Threaded Rod:
Material:Carbon steel(Grade 8.8/10.9),stainless steel(316 SS),or alloy steel.
Thread Type:Metric(e.g.,M20-M64)or UNC/UNF threads.
Protective Sleeve:
Material:HDPE,PVC,galvanized steel,or corrosion-resistant alloys.
Function:Shields the rod from moisture,chemicals,and physical impact.
End Assemblies:
Nuts,washers,and anchor plates(e.g.,square or round plates for load distribution).
Sealing Systems:
Rubber gaskets or epoxy injections at sleeve ends for waterproofing.
3.Working Principle
The sleeved tie rod transfers tensile loads between two structural elements while the sleeve:
Prevents direct contact between the rod and corrosive environments(e.g.,soil,water).
Allows longitudinal movement for thermal expansion or dynamic loading.
Facilitates post-tensioning adjustments via accessible end nuts.
4.Applications
Civil Engineering:
Bridge tie-downs,retaining wall reinforcements,and tunnel linings.
Seismic retrofitting of buildings and historical structures.
Industrial Systems:
Pipeline anchoring,pressure vessel supports,and conveyor frame bracing.
Marine Infrastructure:
Dock pilings,offshore platform braces,and seawall reinforcements.
Utilities:
Suspension systems for pipelines and electrical conduits.
5.Installation Process
Drilling/Coring:
Create holes through structural elements using diamond core drilling.
Sleeve Placement:
Insert the sleeve into the drilled hole,ensuring full penetration.
Rod Insertion&Tensioning:
Pass the threaded rod through the sleeve.
Secure ends with nuts and washers;tension to specified load using torque wrenches or hydraulic jacks.
Sealing:
Seal sleeve ends with epoxy or compression gaskets to prevent ingress of debris/moisture.
6.Advantages
Corrosion Resistance:Sleeve extends service life in aggressive environments.
Load Adjustability:Nuts allow precise tensioning and future re-tensioning.
Electrical Isolation:Non-conductive sleeves(e.g.,HDPE)prevent galvanic corrosion.
Minimal Maintenance:Encapsulated design reduces inspection frequency.
7.Limitations
Complex Installation:Requires precise drilling and sealing techniques.
Cost:Higher initial cost compared to bare tie rods.
Space Requirements:Sleeve diameter is larger than the rod,needing bigger holes.
8.Technical Specifications
Tensile Capacity:50–500 kN(depending on rod diameter and grade).
Sleeve Diameter:Typically 10–50 mm larger than the rod diameter.
Standards Compliance:
ASTM A193(high-temperature steel rods).
ISO 14655(post-tensioning systems for concrete).
EN 10138(prestressing steel components).
9.Innovation Trends
Smart Rods:Embedded fiber-optic sensors for real-time load monitoring.
Hybrid Sleeves:Carbon fiber-reinforced polymers for lightweight high-strength designs.
Self-Healing Sealants:Microcapsule-based sealants自动用心服务cracks.
10.Maintenance&Inspection
Visual Checks:Inspect sleeve surfaces for cracks or UV degradation(every 2–3 years).
Load Verification:Use ultrasonic tension meters to check pre-tensioning levels.
Seal Replacement:Renew end seals if water intrusion is detected.
Conclusion
The Sleeved Tie Rod is an advanced fastening solution combining structural strength with environmental protection.Its dual-component design addresses critical challenges in corrosion-prone or dynamic-load environments,making it indispensable for modern infrastructure projects.Proper installation,material selection,and periodic maintenance are essential to maximize its service life and performance.