- Site Navigation -
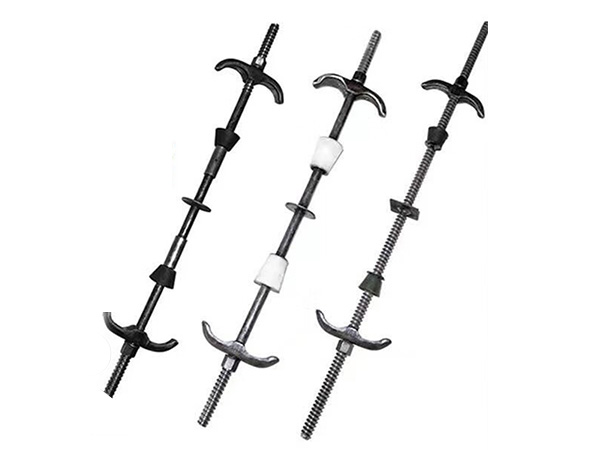

Through-Wall Threaded Rod
A Through-Wall Threaded Rod is a continuous-length fastener with external threading along its entire surface,designed to penetrate walls,slabs,or structural panels for securing obje......
1.Definition&Purpose
A Through-Wall Threaded Rod is a continuous-length fastener with external threading along its entire surface,designed to penetrate walls,slabs,or structural panels for securing objects on both sides.It enables bidirectional load transfer and is commonly used with nuts and washers to create high-strength,adjustable connections in construction,mechanical,and electrical applications.
2.Key Features&Design
Material:
Carbon Steel(Grade 4.8/8.8)for general construction.
Stainless Steel(304/316)for corrosive environments.
Hot-Dip Galvanized Steel for outdoor exposure.
Thread Specifications:
UNC/UNF or Metric Threads(e.g.,M10,M12,M16).
Continuous Threading allows adjustable positioning of nuts and fixtures.
Load Capacity:
Tensile Strength:20–100 kN(varies with diameter and material).
Shear Strength:25–120 kN.
Surface Treatments:
Electroplating,hot-dip galvanizing,or epoxy coating for corrosion resistance.
3.Types&Variants
Fully Threaded Rods:Threading along the entire length for maximum flexibility.
Double-End Threaded Rods:Threaded on both ends with an unthreaded middle section.
Waterproof Through-Wall Rods:Integrated seals or swellable washers for moisture barriers.
High-Strength Rods:Alloy steel rods(e.g.,AISI 4140)for heavy structural loads.
4.Applications
Structural Engineering:
Anchoring steel beams,braces,or brackets to concrete/masonry walls.
Connecting formwork systems in concrete construction.
Mechanical Systems:
Securing pipes,ducts,or equipment through walls.
Supporting HVAC and plumbing installations.
Electrical Installations:
Mounting conduit holders,cable trays,or junction boxes.
Temporary Structures:
Stage rigging,exhibition stands,and temporary fencing.
5.Installation Process
Drilling:
Drill a hole through the wall using a rotary hammer or core drill.
Hole diameter typically 2–4 mm larger than the rod diameter.
Insertion:
Pass the rod through the hole and align it perpendicular to the wall surface.
Securing:
Install washers and nuts on both sides.
Tighten nuts evenly to the required torque(e.g.,40–100 N·m for M12).
Sealing(if needed):
Apply silicone or polyurethane sealant around penetration points for waterproofing.
6.Advantages
Adjustability:Nuts can be positioned anywhere along the rod’s length.
High Load Capacity:Suitable for heavy static and dynamic loads.
Versatility:Compatible with concrete,masonry,wood,and metal substrates.
Cost-Effectiveness:Lower installation cost compared to custom anchors.
7.Limitations
Corrosion Risk:Carbon steel rods require protective coatings in humid environments.
Wall Damage:Penetration may compromise insulation or fireproofing without proper sealing.
Installation Access:Requires access to both sides of the wall for nut tightening.
8.Technical Standards
ISO 898-1:Mechanical properties of carbon and alloy steel fasteners.
ASTM A193:Standard for high-temperature stainless steel threaded rods.
EN 15048-1:Requirements for non-preloaded structural bolting assemblies.
9.Innovation Trends
Smart Rods:Embedded sensors for real-time load monitoring.
Lightweight Designs:Aluminum/composite rods for reduced weight.
Self-Sealing Systems:Rods with pre-applied expandable sealants.
10.Safety&Maintenance
Inspection:Regularly check for corrosion,thread damage,or loosening.
Torque Control:Use calibrated tools to avoid under/over-tightening.
Environmental Compatibility:Select materials based on exposure conditions(e.g.,marine environments require stainless steel).
Conclusion
The Through-Wall Threaded Rod is a fundamental yet highly adaptable fastening solution for cross-wall applications.Its simplicity,strength,and flexibility make it indispensable in construction and industrial projects.Proper material selection,installation precision,and maintenance are critical to ensuring long-term performance and safety.