- Site Navigation -
NEWS LIST
Differences and Application Scenarios Between Construction Jacking Supports and Base Supports
Author:yicheng Date:2025-09-03 14:43:42 Hits:134

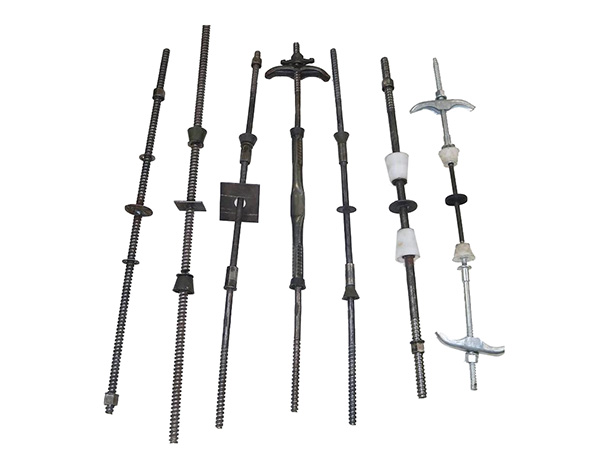
Jacking supports and base supports (also known as "top supports" and "bottom supports" respectively) are both core components of scaffolding support systems. However, they differ significantly in structural design, functions, and application scenarios due to their distinct functional orientations. The specific differences are as follows:
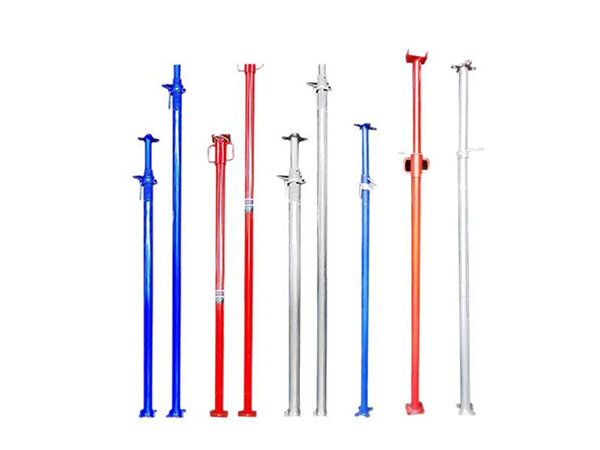
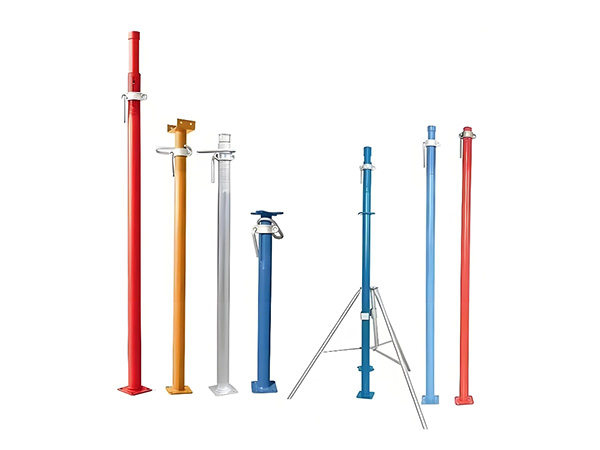
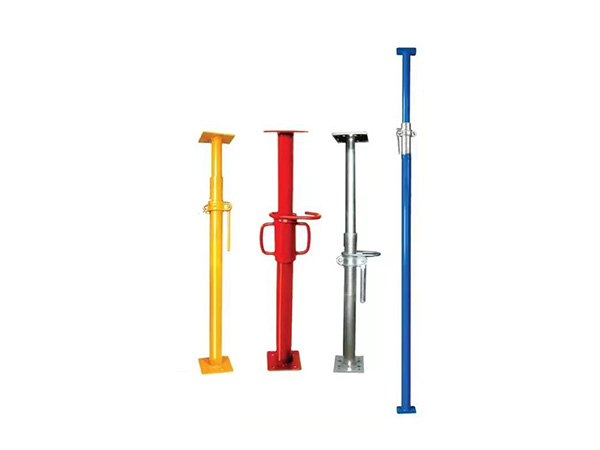
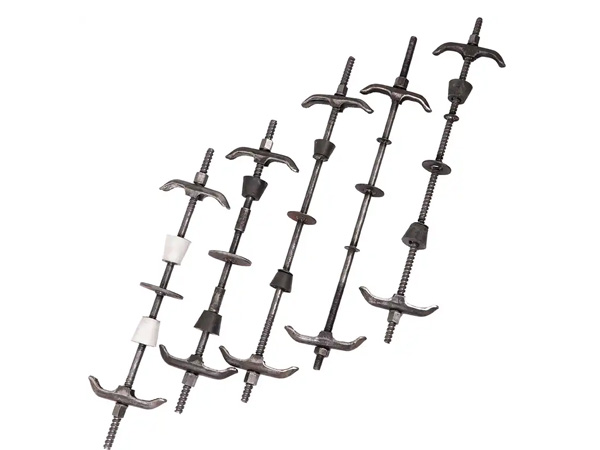
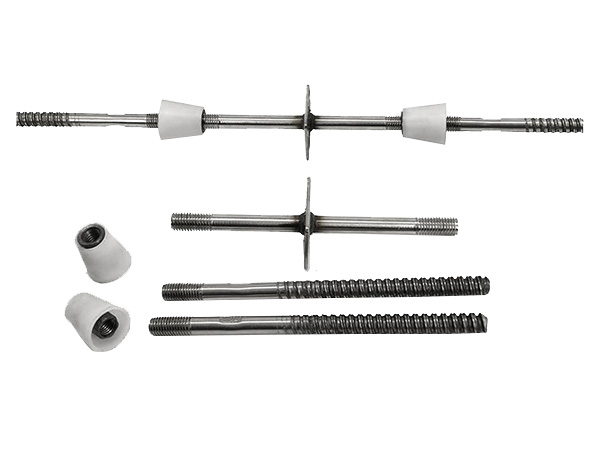
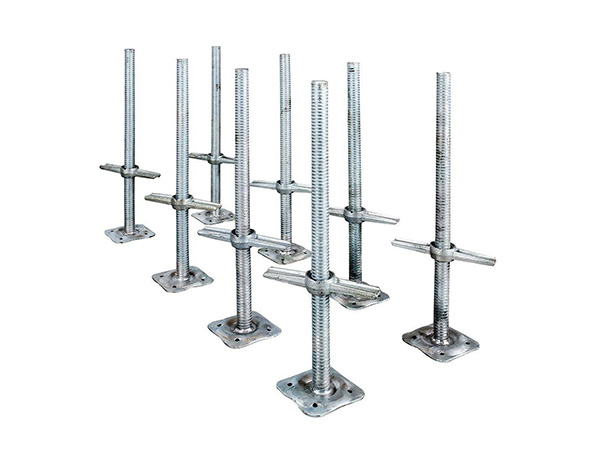
In terms of core functions and structure, a jacking support (top support) primarily connects the scaffolding vertical pole to the formwork and fine-tunes the formwork elevation by adjusting the height of the lead screw, ensuring the flatness of the concrete pouring surface. Its structure typically includes a supporting plate (for bearing the formwork timbers), a lead screw (with an adjusting nut), and an insertion tube (inserted into the top of the vertical pole). Some jacking supports are also equipped with anti-slip gaskets to prevent the displacement of timbers. By contrast, a base support (bottom support) mainly transfers the load of the scaffolding vertical pole to the ground or foundation, reducing the pressure of the vertical pole on the ground and preventing settlement. Its structure is dominated by a "base + lead screw": the base is usually a steel plate (to increase the contact area), and the lead screw can adjust the height of the bottom of the vertical pole to adapt to uneven ground.
Regarding application scenarios, jacking supports are mainly used in the "formwork support stage". For example, in building construction, when pouring floor slabs, beams, and balconies, jacking supports are required to connect vertical poles to the timbers under the formwork. By turning the nuts, the height of the formwork can be adjusted to accurately match the designed elevation. In bridge construction, when pouring box girders and cap beams, jacking supports can be used with cuplock scaffolds or disc-lock scaffolds to fine-tune the curvature and flatness of the formwork. In the secondary lining construction of tunnel projects, jacking supports are also used to fix the lining formwork, ensuring uniform lining thickness.
Base supports, on the other hand, are applicable in the "initial scaffolding erection stage", focusing on solving issues related to "ground adaptation and load transfer". When the ground is uneven (such as the original construction site ground or backfilled areas), the lead screw of the base support can be adjusted to level the entire scaffolding. In scenarios with weak ground bearing capacity (such as indoor decoration or scaffolding erection on floor slabs), the steel plate base of the base support can disperse the load of the vertical pole, preventing damage to the ground or floor slabs. Additionally, during outdoor construction in the rainy season, base supports can be used with backing timbers to prevent vertical poles from directly contacting the waterlogged ground, thereby reducing rusting.
In short, jacking supports focus on "upper formwork adjustment", while base supports emphasize "lower foundation adaptation". The two must be used in conjunction to ensure the stability of the scaffolding support system and construction accuracy.