- Site Navigation -
NEWS LIST
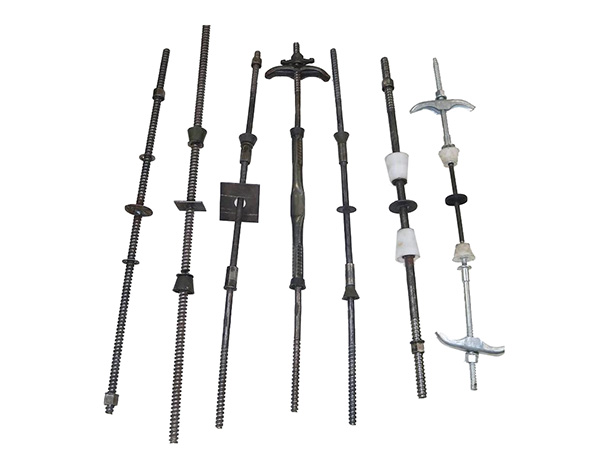
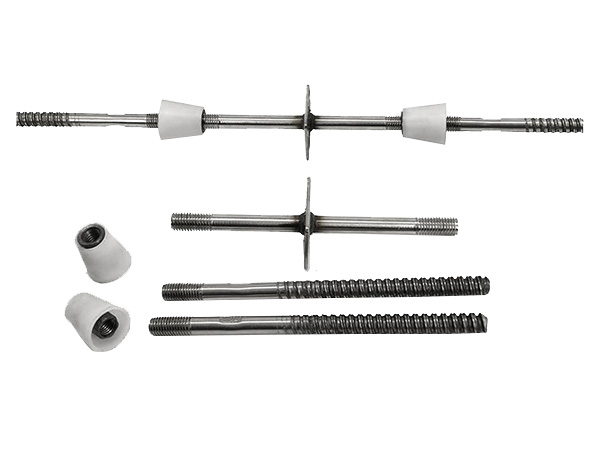
How to Choose Between Solid and Hollow Steel Supports
Author:yicheng Date:2025-09-03 17:57:36 Hits:64

How to Choose Between Solid and Hollow Steel Supports
Solid and hollow steel supports are both widely used in construction,engineering,and infrastructure projects,but their design differences(solid=uniform steel throughout;hollow=empty internal cavity,often cylindrical or rectangular)make them better suited for specific applications.The choice depends on project requirements like load type,weight constraints,environmental conditions,and cost—there is no“one-size-fits-all”option.Below is a structured framework to guide your decision,focusing on key evaluation criteria and real-world use cases.
1.Evaluate Load Requirements:The Most Critical Factor
The type,magnitude,and direction of the load(e.g.,compressive,tensile,bending,or torsional)directly determine whether solid or hollow steel supports are optimal.This is because their structural performance—measured by strength,stiffness,and stability—varies drastically under different loads.
Solid Steel Supports:Strength for High Compression&Torsion
Solid steel’s uniform material distribution makes it excel at handling:
High compressive loads:When the support is pushed downward(e.g.,vertical columns holding heavy concrete slabs,machinery bases).The full cross-section resists crushing,making solid steel ideal for applications where load density is high(e.g.,10,000+lbs per support).
Torsional forces(twisting):In scenarios where the support is rotated(e.g.,shafts in industrial equipment,anchor bolts for wind turbines).The solid core prevents warping or collapse under twist,as there is no internal cavity to weaken torsional resistance.
Point loads or impact:When force is concentrated on a small area(e.g.,support legs for heavy tools,temporary bracing during demolition).The solid structure disperses impact energy more effectively than hollow steel,reducing the risk of denting or cracking.
Hollow Steel Supports:Efficiency for Bending&Light-to-Medium Loads
Hollow steel’s“tube”design leverages the section modulus(a measure of bending resistance)to perform well in:
Bending loads:When the support is pulled or pushed sideways(e.g.,horizontal beams in scaffolding,handrails,or bridge guardrails).Most of a material’s bending strength comes from its outer fibers—hollow steel retains this outer strength while removing unnecessary inner material,making it nearly as stiff as solid steel for bending but much lighter.
Light-to-medium compressive loads:For applications where weight is a priority and loads are moderate(e.g.,vertical supports in temporary shelters,retail display structures,or residential mezzanines).Hollow steel can handle compressive forces effectively if the cavity is properly reinforced(e.g.,with internal bracing for long spans).
Distributed loads:When weight is spread across the support(e.g.,floor joists in lightweight industrial buildings).The hollow design’s uniform cross-section ensures even load distribution without excessive material use.
2.Consider Weight and Installation Practicality
Weight impacts everything from transportation costs to on-site handling(e.g.,requiring cranes vs.manual labor)and the overall structural load of the project(e.g.,supporting a lightweight scaffold vs.a heavy building).
Solid Steel:Heavier per unit length due to its full material composition.This makes it:
Less practical for large-scale projects or tall structures(e.g.,20+foot supports),where weight adds up and increases foundation requirements.
More challenging to install manually—often requiring heavy machinery(cranes,forklifts)to move and position.
Suitable only for small,localized supports(e.g.,1–3 foot anchor posts)where weight is not a constraint.
Hollow Steel:Significantly lighter(30–60%less weight than solid steel of the same outer dimensions)because of its internal cavity.This makes it:
Ideal for projects where weight savings are critical(e.g.,mobile scaffolding,temporary event structures,or aerial platforms),as lighter supports reduce transportation costs and simplify manual installation.
Better for tall or long-span applications(e.g.,10+foot beams in warehouses),where lighter weight eases stress on foundations and adjacent structures.
Easier to handle on-site—many hollow steel supports can be carried by 1–2 workers,reducing reliance on heavy equipment.
3.Assess Environmental Conditions
Steel’s durability depends on its ability to resist corrosion,moisture,and temperature extremes—factors that differ between solid and hollow designs,especially for outdoor or harsh-environment projects.
Solid Steel:More resistant to corrosion in exposed settings(e.g.,outdoor construction,coastal areas)for two reasons:
No internal cavity to trap moisture,salt,or debris(which cause hidden rust in hollow supports).
A thicker cross-section means even if surface corrosion occurs,the core material remains intact,preserving strength.
Note:Solid steel still requires protective coatings(e.g.,galvanization,paint)for long-term outdoor use,but it has a longer service life than unprotected hollow steel.
Hollow Steel:Requires extra precautions in harsh environments due to its internal cavity:
Moisture,salt,or chemicals can seep into the cavity(e.g.,through small gaps in joints)and cause internal corrosion—this rust is invisible from the outside and can weaken the support over time.
To mitigate this,hollow steel must be:
Sealed at both ends(e.g.,with plastic caps or welded plates)to prevent debris/moisture entry.
Coated internally(e.g.,with anti-corrosion sprays)in high-risk areas(coastal,industrial,or wet climates).
Hollow steel performs well in indoor,dry environments(e.g.,warehouses,retail spaces)where corrosion risk is low.
4.Compare Cost:Material and Total Project Expenses
Cost is a practical consideration,but it’s not just about the upfront price of the steel—you must also factor in transportation,installation,and maintenance costs.
Solid Steel:Higher upfront material cost because it uses more steel per unit length.Additionally:
Heavier weight increases transportation costs(e.g.,more fuel for trucks,larger shipping containers).
Requires more labor or machinery for installation,adding to on-site costs.
Lower maintenance costs long-term(less risk of hidden corrosion),but this may not offset higher initial expenses for most projects.
Hollow Steel:Lower upfront material cost(uses less steel)and total project cost for most applications:
Lighter weight reduces transportation and handling costs—you can ship more supports per load,and installation requires fewer workers or no heavy machinery.
Maintenance costs are higher only if additional corrosion protection(e.g.,sealing,internal coatings)is needed;in dry indoor settings,maintenance costs are minimal.
For projects where weight and cost are priorities(e.g.,temporary structures,lightweight buildings),hollow steel is almost always the more economical choice.
5.Match to Project Type:Real-World Use Cases
To simplify decision-making,here are common scenarios where one design is clearly preferred over the other:
Choose Solid Steel Supports When:
The support bears high compressive loads(e.g.,vertical columns for heavy industrial machinery,concrete slab foundations).
The application involves torsion or impact(e.g.,anchor bolts,tool bases,demolition bracing).
The support is small(1–3 feet long)and weight/installation ease are not concerns.
The environment is harsh(coastal,wet,or industrial)and long-term corrosion resistance is critical(with proper coating).
Choose Hollow Steel Supports When:
The support handles bending or light-to-medium compressive loads(e.g.,scaffolding beams,handrails,mezzanine columns).
Weight savings are critical(e.g.,mobile structures,tall spans,aerial platforms).
The project is indoor or low-corrosion(e.g.,warehouses,retail spaces,office buildings).
You want to reduce total project costs(material,transportation,installation).
Final Checklist for Decision-Making
Before choosing,confirm these four points:
What type of load(compression,bending,torsion)will the support handle,and what is the load magnitude?
Is weight a constraint(e.g.,manual installation,tall spans,mobile structures)?
Will the support be exposed to harsh conditions(moisture,salt,chemicals)that require corrosion protection?
What is the budget for material,transportation,and maintenance?
By aligning these factors with the strengths of solid or hollow steel,you ensure the support is safe,efficient,and cost-effective for your project.