- Site Navigation -
NEWS LIST
Connection Methods Between Adjustable Screw Jack Brace and Scaffold Uprights/Transoms
Author:yicheng Date:2025-09-03 15:26:28 Hits:149
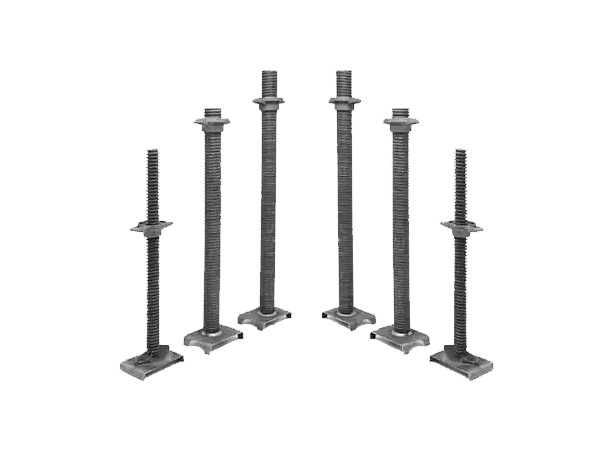

Connection Methods Between Adjustable Screw Jack Brace and Scaffold Uprights/Transoms
The connection between the Adjustable Screw Jack brace and scaffold uprights/transoms must ensure stability and load transfer efficiency.The connection method depends on the scaffold type(e.g.,coupler-type,cup-lock,ring-lock)and adjustment requirements.Connections can be categorized into two types:connections to uprights(core load-bearing)and connections to transoms(auxiliary stabilization).Details are as follows:
1.Connection to Scaffold Uprights(Core Load-Bearing)
Uprights are the primary load-bearing components of scaffolds.The connection between the top brace and uprights must directly transfer vertical loads and is the core node of the support system.Main connection methods include:
1.1 Insertion Connection(Most Common)
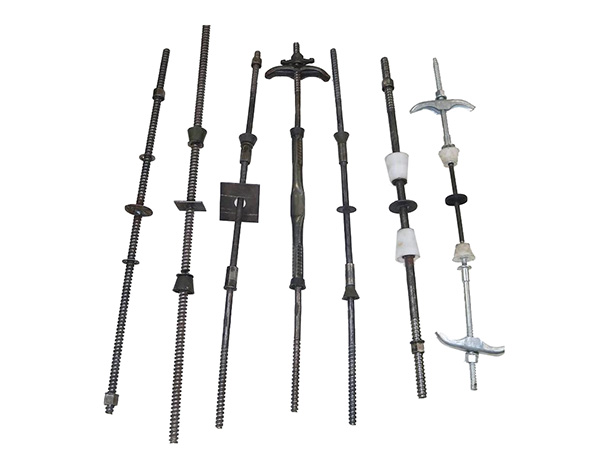
The bottom of the top brace is designed as an"insertion tube"structure(tube diameter slightly smaller than the inner diameter of the upright,typically by 2-3 mm).It is directly inserted into the top of the scaffold upright and secured via positioning pins/holes or anti-slip bolts to prevent rotation or slipping under load.
Applicable Scenarios:Coupler-type steel tube scaffolds(φ48 mm uprights),cup-lock scaffolds.Suitable for most civil building floor slabs and beam pouring support.
Advantages:Easy installation,quick height adjustment(via threaded rotation),and clear load transfer path to the upright.
Note:The insertion depth must comply with standards(typically≥150 mm)to avoid instability due to insufficient depth.
1.2 External Clamp Connection(Heavy-Duty/Special Uprights)
The bottom of the top brace is equipped with a"clamp-type"fixture(comprising two arc-shaped steel plates and bolts)that tightly fastens the upright from the outside without inserting into the upright.It accommodates a wider range of upright diameters(e.g.,φ48 mm,φ60 mm).
Applicable Scenarios:Uprights with obstacles at the top(e.g.,transom connectors),temporary top brace installation,or heavy-duty support(e.g.,large-span beams,floor slabs).
Advantages:Does not damage the upright structure,can be installed at any height,adjustable clamping force,suitable for scenarios with significant load fluctuations.
Note:High-strength bolts(e.g.,Grade 8.8)must be used,and anti-slip pads should be added at the clamp-upright contact points to prevent slipping.
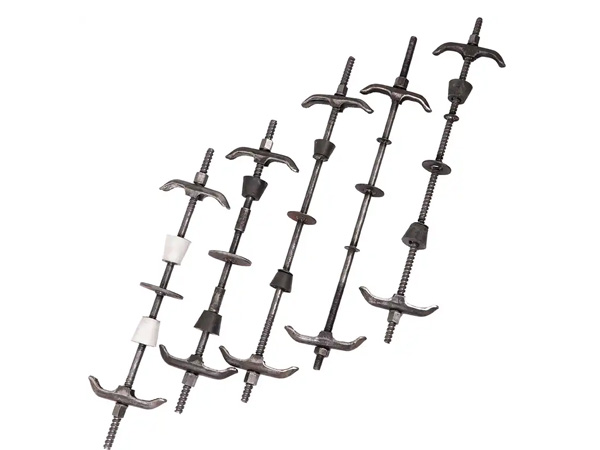
1.3 Threaded Connection(Dedicated for Ring-Lock/Cup-Lock Scaffolds)
The top of ring-lock or cup-lock scaffold uprights is pre-threaded(internal threads),and the bottom of the top brace is designed with matching external threads(e.g.,M30,M36).The top brace is directly screwed into the upright top without additional fasteners.
Applicable Scenarios:Ring-lock steel tube scaffolds(e.g.,Q355 steel uprights),cup-lock scaffolds.Commonly used in standardized construction(e.g.,municipal bridges,high-rise buildings).
Advantages:High connection precision,excellent thread self-locking,strong anti-pullout capacity(can withstand vertical tension),and high disassembly/assembly efficiency,suitable for batch reuse.
Note:Clean debris(e.g.,mortar,rust)from the threads before installation to avoid connection failure due to thread damage.
2.Connection to Scaffold Transoms(Auxiliary Stabilization)
Transoms primarily enhance the overall stability of scaffolds.The connection between the top brace and transoms provides"auxiliary constraint"to prevent tilting under horizontal loads(e.g.,pouring impact,wind loads).Common methods include:
2.1 Coupler Fixation(Universal)
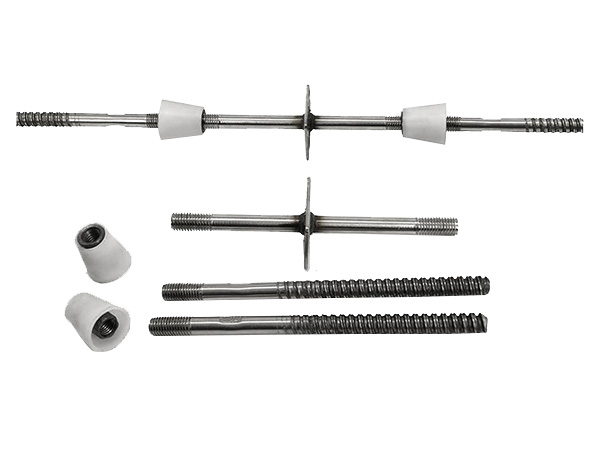
A short steel tube(length~100-150 mm,diameter matching the transom,e.g.,φ48 mm)is welded to the"screw part"or"below the baseplate"of the top brace.This short tube is clamped to the scaffold transom via right-angle couplers to form horizontal constraint.
Applicable Scenarios:Coupler-type and cup-lock scaffolds,especially for scenarios with significant horizontal loads(e.g.,wall pouring,high-formwork support).
Advantages:High versatility,utilizes existing scaffold couplers,no need for custom parts,adjustable constraint strength(by tightening coupler bolts).
Note:The short tube must be fully welded to the top brace(weld height≥6 mm)to avoid constraint failure due to weld fracture.
2.2 Slot Connection(Dedicated for Ring-Lock Scaffolds)
The end of ring-lock scaffold transoms has built-in"plugs,"and the bottom or middle of the top brace screw is pre-equipped with"slots"(matching the ring-lock node specifications).The transom plug is directly inserted into the top brace slot and secured via the transom’s spring pin for rapid connection.
Applicable Scenarios:Ring-lock scaffolds,suitable for standardized and rapid construction projects(e.g.,prefabricated buildings,large factories).
Advantages:Bolt-free operation,fast disassembly/assembly(can be done by one person),high slot-plug matching precision,and strong horizontal constraint stability.
Note:Ensure the spring pin is fully engaged in the slot to avoid plug dislodgement due to vibration,and transoms must be connected perpendicularly to the top brace(avoid oblique forces).
3.Core Principles for Selecting Connection Methods
Match Scaffold Type:Coupler-type scaffolds prioritize"insertion connection+coupler fixation";ring-lock scaffolds prioritize"threaded connection+slot connection."Avoid mixing配件across types.
Prioritize Load-Bearing Nodes:The connection between the top brace and upright must meet load requirements(e.g.,insertion depth,thread strength).Transom connections are auxiliary and cannot replace the core load-bearing role of uprights.
Comply with Standards:All connections must follow standards such as Technical Code for Safety of Steel Tube Scaffolds in Construction(JGJ130),e.g.,coupler bolt tightening torque must be 40-65 N·m,insertion depth≥150 mm,to ensure node safety.