- Site Navigation -
NEWS LIST
How to Choose the Right Wall-Tie Bolt for Cavity Wall Construction?
Author:yicheng Date:2025-09-03 16:51:04 Hits:168

Choosing the right wall-tie bolt for cavity wall construction is crucial for ensuring structural stability,durability,and safety.Here’s a comprehensive guide to help you make an informed decision:
1.Understand Cavity Wall Basics
A cavity wall consists of two separate walls(typically masonry)with a gap(cavity)between them,often used for insulation,moisture control,and thermal efficiency.
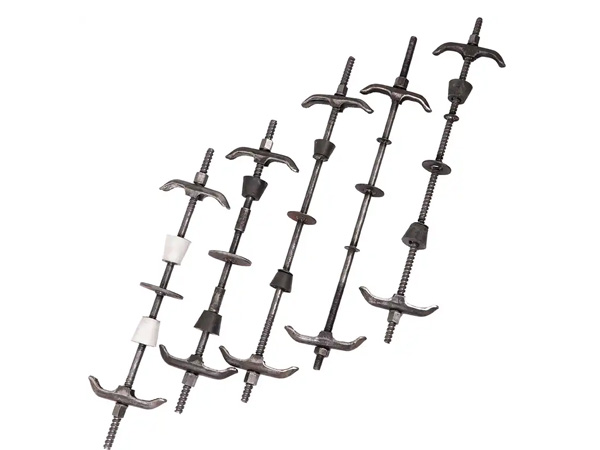
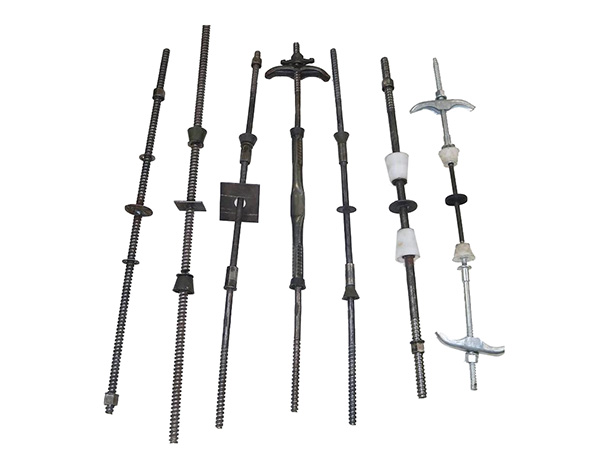
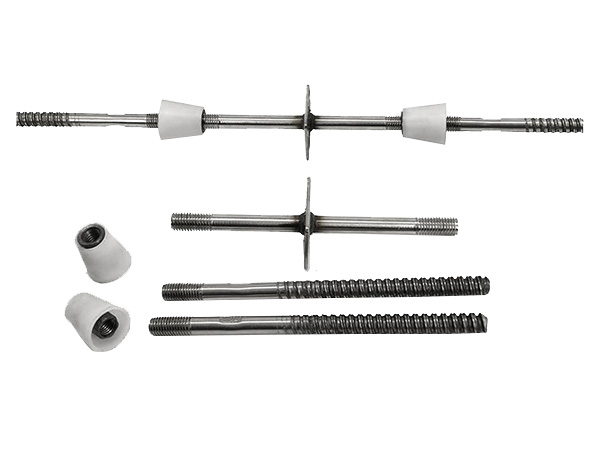
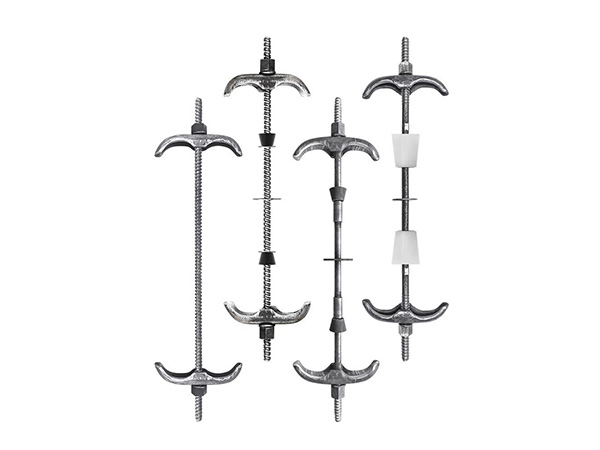
Wall-tie bolts(also called cavity wall ties)are metal or composite components that connect the inner and outer layers of the wall,providing structural cohesion while allowing for movement and preventing moisture transfer.
2.Comply with Standards and Regulations
Ensure the wall-tie bolts meet relevant national or international standards.For example:
SANS 28:1986(South African Standard)specifies dimensions and materials for metal ties in cavity walls.
Other regions may have local codes(e.g.,ASTM in the U.S.,EN in Europe)governing tie strength,corrosion resistance,and installation.
Standards often cover load-bearing capacity,materials,and durability requirements.
3.Material Selection
Stainless Steel:Highly resistant to corrosion,suitable for humid or aggressive environments.Grades like 304 or 316 are common.
Galvanized Steel:Economical but less corrosion-resistant than stainless steel.Suitable for drier climates.
Composite Materials(e.g.,basalt,fiberglass):Lightweight,corrosion-proof,and thermally efficient,but may have lower fire resistance.
Choose based on environmental conditions and project requirements.
4.Dimensions and Load Capacity
Select ties of appropriate length to span the cavity width and embed sufficiently into both wall layers(typically 50-100 mm per side).For example:
Cavity width+embedment depth=total tie length.
Ensure the tie can handle expected loads(e.g.,wind pressure,structural movements).Standards like SANS 28 provide guidelines on load capacities .
5.Design and Type of Tie
Flexible Ties:Allow movement between wall layers,reducing stress from thermal expansion or settling.Ideal for areas with seismic activity or temperature variations.
Rigid Ties:Provide firm connections but may not accommodate movement as well.
Specialized Ties:For example,"Brolly"anchors or expanding bolts for hollow walls(e.g.,drywall,plasterboard).
6.Installation Considerations
Spacing and Pattern:Follow codes for vertical and horizontal spacing(e.g.,typically 600-900 mm horizontally and 300-450 mm vertically).
Embedment Depth:Ensure ties are fully embedded in mortar joints(min.50 mm depth)for solid masonry,or use mechanical anchors for hollow blocks.
Corrosion Protection:Use ties with protective coatings(e.g.,zinc)in corrosive environments.
7.Retrofitting and Repair
For existing walls,use retrofit ties designed for easy installation(e.g.,screw-in or resin-bonded ties).
Inspect old ties for corrosion or failure,especially in older buildings,and replace with compatible materials.
8.Environmental and Thermal Efficiency
Composite ties(e.g.,fiberglass,basalt)reduce thermal bridging,improving insulation performance.
Avoid metals in high-moisture areas without corrosion protection to prevent deterioration.
9.Quality and Verification
Purchase from reputable suppliers and verify certifications(e.g.,SANS 28:2010 for quality testing).
For critical projects,consult structural engineers to ensure ties meet design loads and safety factors.
Summary of Key Considerations:
Cavity Width:Measure accurately to choose correct tie length.
Environment:Select materials resistant to local conditions(e.g.,humidity,salinity).
Load Requirements:Match tie strength to structural demands(e.g.,high-rise vs.low-rise buildings).
Compliance:Adhere to regional standards and building codes.
By evaluating these factors,you can select wall-tie bolts that ensure safety,durability,and performance in cavity wall construction.For detailed standards or product specifications,refer to resources like SANS 28 2 or manufacturer guidelines.